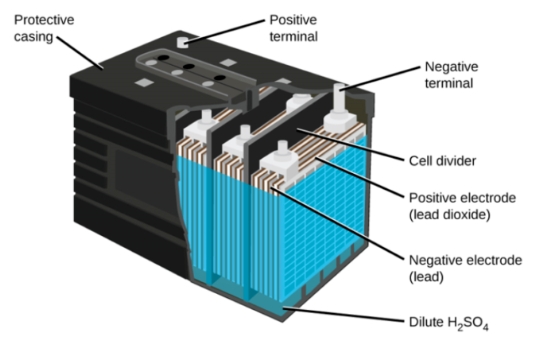
Lead Acid Battery has always been one of Mk Energy’s core battery series. As our technology advances and users’ needs diversify, various lead-acid battery types have emerged. In this guide, we will introduce you to the three main types: VRLA, AGM, and gel batteries. By understanding the characteristics of each product, you can choose according to different application areas.
Lead Acid Battery: VRLA Batteries
The VRLA battery is a rechargeable lead acid battery with a sealed design and maintenance-free operation and is widely used in various applications. One of its distinguishing features is its sealed construction. Unlike traditional flooded lead-acid batteries, VRLA batteries are designed with valves that regulate the release of excess gas produced during charging. This sealed design requires no regular maintenance, making VRLA batteries a popular choice for applications where accessibility is limited or maintenance is impractical. Another key feature is its versatility, which provides design and installation flexibility so that it can be installed in various locations without performance issues. Widely used in uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems, telecommunications equipment, and renewable energy storage.
The optimal operating temperature of VRLA batteries is 25°C, and every 8°C above this temperature threshold reduces battery life by half. Batteries perform best when discharged slowly, with capacity readings at slower discharges being significantly higher than at the 1C rate.
Lead Acid Battery: AGM battery
An AGM battery uses fiberglass mat separators to absorb and hold the electrolyte. The pad is filled with electrolytes that are efficiently and evenly distributed throughout the battery. The AGM design prevents the free flow of electrolytes, making the battery spill-proof and suitable for applications where safety and minimal maintenance are a priority. Its design minimizes internal resistance, allowing fast discharge and charge cycles without compromising performance. It is best used as a medium-sized battery with a capacity of 30 to 100Ah. This characteristic also makes AGM batteries ideal for starting batteries in motorcycles and start-stop functions in micro-hybrid vehicles.
Lead acid battery: GEL battery
GEL battery is also a type of lead-acid battery. Its most prominent feature is the use of silica gel as an electrolyte. Optimum operating temperature range: -20℃~55℃. This gel secures the electrolyte within the battery, prevents spillage, and allows for versatile positioning in different directions without affecting performance. Gel electrolytes also minimize stratification and ensure ions are evenly distributed throughout the cell, improving overall efficiency. At the same time, GEL batteries strongly resist vibration and impact. Combining this feature with an anti-spill design makes gel batteries ideal for solar systems, emergency power supplies, UPS, and other applications.
Design and structure comparison
VRLA, AGM, and GEL batteries are three different types of lead-acid batteries, all of which share the common features of being maintenance-free and sealed. The main difference lies in the electrolyte medium used within each cell. AGM batteries utilize fiberglass mats to absorb and immobilize the electrolyte. This design enhances the high-discharge characteristics of AGM batteries, making them suitable for applications requiring rapid bursts of energy. GEL batteries, on the other hand, use silicon-based gel to provide good resistance to vibration and shock. Both designs prevent electrolyte spillage, making them suitable for applications where safety and maintenance are critical.
How to maintain them?
Charge them according to manufacturer specifications and avoid overcharging, which can cause overheating and accelerated aging. Use a quality charger with voltage regulation to prevent damage. Check the charging voltage regularly to ensure it meets the battery’s requirements. Keep battery terminals clean and free of corrosion. If corrosion is present, use baking soda and water to clean the terminals. Make sure connections are tight to prevent resistance and overheating. Check the entire battery regularly for any signs of damage or leaks.
AGM batteries may require regular watering, unlike GEL batteries but less frequently than traditional flooded lead-acid batteries. Check water levels regularly, especially in hot environments. Periodically monitor the battery’s voltage, state of charge, and overall condition. Implement a routine inspection program to detect any damage, leaks, or signs of unusual behavior.
Ultimately
There are various types of lead-acid batteries. This article introduces the characteristics of VRLA, AGM, and GEL batteries to popularize relevant knowledge for our users to make the right choice. Whether it’s maintenance-free operation, precise power delivery, or deep cycle capabilities, they have what you need.